LEED O+M CERTIFICATION:
A Commitment to Continuity
By Arq. Hanna Zermeño | Property Mgt. Coordinator and Customer Service at American Industries Group®
By Biol. Pablo Ramírez | Environmental, Health and Safety Supervisor at American Industries Group®

Published 05/31/2022
As a company that is proud to uphold ESG values (Environmental, social, and governance), American Industries Real Estate is participating in the process of obtaining LEED O+M certification for seven industrial facilities in Mexico. Together these facilities represent 1,096,633 square feet and are expected to obtain Silver and Gold certification.
Four levels of LEED certification
Eight categories were established for minimizing environmental impacts, each of which outline prerequisites and credits that count as points towards the overall rating to obtain the desired LEED certification level. Below are the categories and actions for which projects can earn points:
- Location and transportation. Incentivize the use of alternative methods of transport (bicycles, hybrid cars, public transportation).
- Sustainable sites. Avoids sedimentation and erosion of the external environment, promotes habitat restoration and management of water runoff, among other strategies.
- Water efficiency. Optimal use of water, including intake , treatment, reuse, savings, and proper disposal.
- Energy and atmosphere. Aimed at optimal energy use, the source of this, and the efficiency of its impact on the community (this category is where the most number of credits can be earned for the overall LEED score).
- Materials and resources. Involves employing reused materials and properly managing waste.
- Indoor environmental quality. Promotes strategies that impact the health and wellbeing of building occupants, including controlling indoor pollution, maintaining a comfortable temperature, etc.
- Continual improvement of strategies implemented.
- Regional priority. Promotes the sustainable development of strategies implemented.
What is LEED O+M?
The LEED O+M rating system is a set of performance standards. This rating system encourages property owners and users to implement sustainability best practices and reduce the environmental impact of buildings throughout their useful life.
The LEED O+M rating system includes the following specific areas:
- Exterior maintenance of the building
- Water efficiency
- Energy efficiency
- Use of green cleaning products and implementation of ecological practices for cleaning and building modifications
- Waste management and sustainable purchasing practices
- Management of indoor environmental quality
- Operating policies, programs, and plans for current operations
- Regional considerations
- Innovation in operations
Where did LEED O+M come from?
Today there are several certifications aimed at extending the useful life of buildings and decreasing their environmental impact. Among these certifications is the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design certification, better known as LEED, the most recognized certification in the Americas.
In best-case scenarios, if a building is constructed according to certification parameters, such as LEED standards, and is well-designed, updated, and maintained, its useful life can be extended exponentially. However, certifications like LEED are relatively recent programs developed only towards the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th. This means that many existing buildings were designed and constructed without receiving a sustainable certification.
A building can be considered a living entity with a useful life that can be extended or shortened depending on how it is maintained and managed.
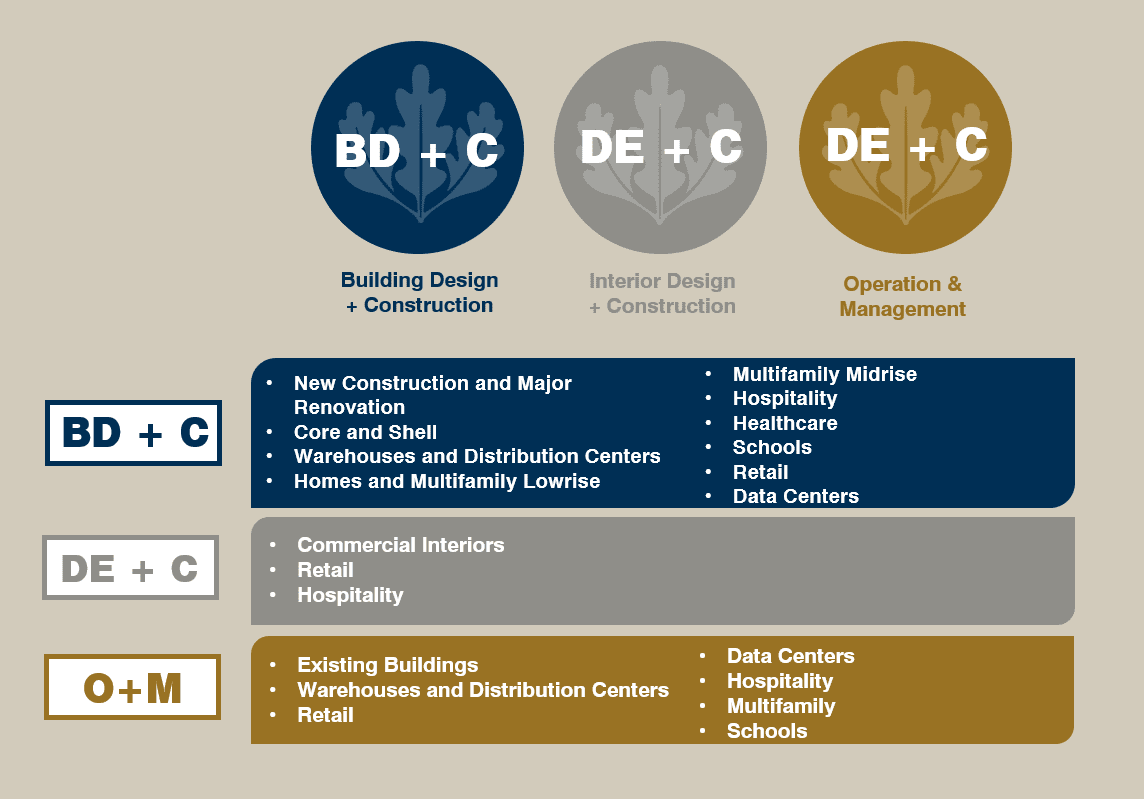
In the early 2000s, the USGBC (U.S. Green Building Council) recognized this need to certify and improve the efficiency and useful life of existing buildings. This change was a breakthrough for LEED certifications. In addition to the certification known as LEED BD+C (Building Design and Construction), the certification for existing buildings LEED O+M (Operations and Maintenance), three other certifications were also added: LEED ID+C (Interior Design and Construction), LEED Residential, LEED C+C (Cities and Communities) and LEED Recertification.
These changes in LEED certification were aimed at including all the transformational phases of the construction process, outlining them in hundreds of green assessment tools developed to measure the sustainability objectives in the construction sector and compare operational and management best practices and other green certification standards.
Several factors are considered to improve an existing construction and certify it for the first time, such as the building’s current use, its proper operation, consumables, wastes, users, and social and environmental impacts.
What is the goal of LEED O+M?
In this context, the LEED rating system also aims to assess and classify buildings depending on their energy and environmental requirements. The LEED O+M system offers existing buildings an opportunity to improve their operations and complete care of the property. To obtain a certificate with LEED O+M, the property must have been in operation and fully occupied for at least one year. The implementation project could include improvements, with little or no construction.
LEED O+M is geared towards implementing sustainable strategies and focuses on maintaining high-performance buildings. It is important to consider that it can take up to 80 years to compensate for the environmental impacts of demolishing an existing building and building a new one, even if the new one is highly energy efficient. Even though there are many old buildings around the world that are considered to be inefficient and continue exhausting resources, the efficiency of building operations and their maintenance can be improved by implementing the practices and suggestions outlined in LEED O+M certification parameters.
“It’s imperative to consider the impact the construction industry has on the environment, using various materials and sources during a building’s entire life cycle.”
American Industries Real Estate is committed, on a local and global scale, to doing its part to minimize environmental impacts and continue promoting the philosophy of caring for, maintaining, and repairing the environment to restore its original balance.
How can I obtain LEED O+M certification?
If you would like to learn more about how to obtain this certification, please reach out to American Industries Real Estate’s Property Management division and we would be happy to assist you.
“YOU CAN’T IMPROVE WHAT YOU DON’T MEASURE.”
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE